Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in locating the source of a medical problem along with providing the information needed to help diagnose a wide variety of conditions.
In this blog, we explore the difference between an MRI and a CT scan. The aim is to help you understand why your doctor has recommended it, what they are used for and how they work.
Private diagnostic imaging at a glance:
- Appointment within 2 weeks
- Prices start from £334
- Available at a range of our UK locations
Call us on: 0330 818 8945
What is the difference between an MRI and a CT scan?
Both MRIs and CT scans are medical imaging methods that are used to create images of the internal body to help diagnose a range of different medical conditions.
The main difference between these two diagnostic imaging techniques is that an MRI uses strong magnetic fields to take images, while a CT scan uses x-rays.
MRI scan explained
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. During an MRI scan, you will be asked to lie down inside a long open tunnel which is the MRI scanner. This machine then uses radio waves that bounce off fat and water molecules in your body. These signals are sent to a computer to create an image of the affected area.
CT scan explained
CT stands for Computed Tomography. Sometimes CT scans are referred to as CAT scans which stands for Computed Axial Tomography.
The process is similar to an MRI as you will be asked to lie on a moving table that takes you through the circular CT scanner. However, this machine uses x-rays to take cross-sectional images of certain body parts from different angles. These 2D images are then sent to a computer where they are transformed into 3D images.
Please note that CT scans are not available at Practice Plus Group.
What do MRI and CT scans show?
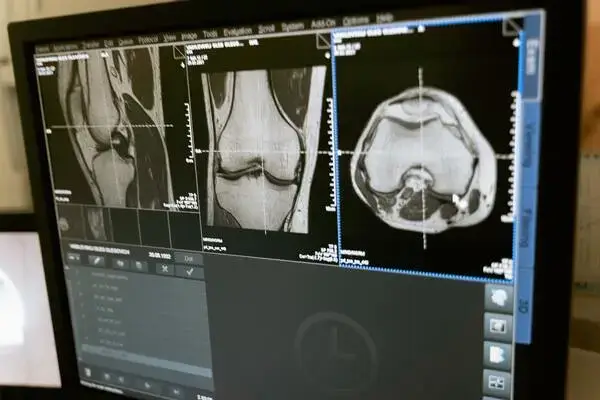
Both MRI and CT scans show a detailed view of different parts of your body. MRI scans are generally considered as providing more accurate imagery and are therefore used for diagnosing conditions associated with your bones, organs or joints. CT scans are often used to identify any bone fractures, tumours, or internal bleeding.
Reasons for getting an MRI scan could include:
- torn ligaments
- soft tissue problems
- spinal problems
- nerve issues
- inflammation.
Reasons to have a CT scan include:
- emergency diagnoses e.g. strokes
- fractured bones
- joint issues
- blood clots
- injuries to internal organs
- internal bleeding
- tumours
- cancer development.
What can a CT scan show that an MRI cannot?
CT scans are often used in emergency situations as they produce faster results. This enables doctors to provide faster diagnosis and treatment. For example, CT scans can be used when looking at blood vessels to diagnose the cause of a stroke.
CT scan vs MRI – the costs
MRI scans typically cost more than CT scans and produce more detailed images.
A full breakdown of private MRI scans at Practice Plus Group is available above.
Please note that CT scans are not available at Practice Plus Group.
CT vs MRI – the procedure
The process for both procedures is similar: you will be asked to lie down on a bed that will then slowly and automatically slide into the circular scanner. This table will move up and down to produce images of different parts of your body. The radiographer will leave the room once you are in the scanner, but you will be able to communicate with them through an intercom.
You will need to stay as still as you can to ensure accurate pictures are taken. You may be asked to hold your breath during the scan.
The main difference between the two procedures is that a CT scan is much quieter than an MRI. MRI scans are noisy and to manage this, you will be given earplugs and headphones to listen to relaxing music during your scan.
An MRI scan might take around an hour to complete, whereas a CT scan can take as little as ten minutes.
Pros and cons of CT scans vs MRI
While both procedures are considered to be very safe, there are some disadvantages to consider.
MRI advantages
- MRI scans produce more detailed images
- MRI scans do not use radiation
- MRI images can help to identify issues in the soft tissues, joints, organs, brain and heart.
MRI disadvantages and risks
- MRI scans create loud noises which some people may find stressful
- metal objects, jewellery and clothing must be removed before the scan
- medical or metal implants may interfere with the MRI scan (e.g. artificial hip replacements, pacemakers, IUDs, surgical clips, metal plates or insulin pumps) so you should always let the doctor know about them when they are deciding which test to send you for
- those who suffer from claustrophobia may find the machine uncomfortable
- sometimes contrast dye is used which can cause an allergic reaction in a small number of people.
CT scan advantages
- CT scans are less expensive than MRI scans
- CT scans don’t last as long as MRI scans and can be used for speedy diagnosis in emergency situations
- CTs can help to identify issues in soft tissue such as internal bleeding, as well as tumours, cancer development and fractures
- your whole body doesn’t enter the CT scanner, so you are less likely to feel claustrophobic.
CT scan disadvantages and risks
- a CT scan involves a small dose of ionising radiation. There is a very small risk this could increase your chance of developing cancer later in life
- CT scans are not usually recommended for pregnant women unless in an emergency
- sometimes contrast dye is used which can cause an allergic reaction in a small number of people.
Which is better: MRI or CT scans?
It isn’t a question of one method being better than the other, but more: which method is better suited to your specific needs. The right procedure for you will depend on the area of the body or the type of issue you are trying to diagnose or pinpoint.
For example, if your doctor thinks you might have fractured your arm – a CT scan might be a better option. Whereas, if you have a problem with your spine, or an issue which is harder to diagnose, a more detailed MRI scan might be necessary. In emergency situations, a CT scan might be chosen as it provides faster results.
Risk factors also play a part in which method is offered. For example, those with metallic implants may not be suitable candidates for an MRI. Your doctor will be able to advise on the right scan for you.
Please note that CT scans are not available at Practice Plus Group.
Choose the right treatment for you
We understand how important it is to get the right diagnosis as quickly and easily as possible. Diagnostic imaging can provide the information radiologists and doctors need to find the source of your pain and start treatment.
Here at Practice Plus Group, we offer personalised diagnostic procedures with short waiting times and excellent quality of care.
MRI scan vs CT scan FAQs
Not yet found what you’re looking for? Our dedicated FAQs might be able to help.
No. MRI and CT scans use different technology to create diagnostic images of your body. MRI uses radio waves, while CT uses x-rays.
CT scans are used to diagnose different conditions than MRI scans. For example, if you had a suspected fracture, a CT scan is more suitable for finding the problem. They are also more suited to emergency situations as the results are quicker.
An MRI scan can produce more detailed images of tissues and organs than a CT scan. An MRI scan may be used to diagnose issues with soft tissue, joints, organs, the brain and the heart.
MRI scans are more expensive than CT scans as the equipment is more costly and the process takes longer.
Those with severe claustrophobia may find both procedures uncomfortable.
An MRI scan produces loud banging, clanking and whirring sounds which might be overwhelming for some patients. MRI scanners are also more enclosed than CT scanners which are more doughnut-shaped.
Both imaging methods are very low risk. CT scans involve a very small amount of radiation during the imagine process, but this poses a very low risk to your health.